LMM BLOG
SOME CONSIDERATIONS ON INFLATION DEVELOPMENTS
What happened?
Over the last 20 years, the financial markets have been characterised by steadily falling interest rates. The actions and programs of central banks and governments have supported the investment markets in the sense of the often cited “Fed put”.
The significant decline in interest rates was accompanied by an increase in valuations and prices of most asset classes, which resulted in above-average positive investment results in recent years. Although there were some references to possible side effects, very few expected the environment to change as early as this year.
How is inflation measured?
In order to measure price developments, a so-called “basket of goods” is defined. The composition of the basket of goods is based on the real expenditure of an average household. In Switzerland, the basket of goods is called the national consumer price index (CPI). Around 100,000 prices are surveyed every month to measure price trends.

LCI shopping cart and weights 2022 Source: bfg.admin.ch
Are there differences in inflation measurement from a global perspective?
The calculation methods and coverage of the national consumer price indices can differ significantly from country to country. An international comparison of inflation based on the national indices is therefore very difficult. For this reason, the member states of the European Union (EU) have introduced an indicator – the harmonized index of consumer prices (HICP). When making comparisons using the HICP, however, it is important to note that the value per good and service varies from country to country.
What is core inflation?
When measuring price developments, certain goods have a greater influence. Therefore, so-called core inflation is additionally calculated, which excludes certain goods of the basket of goods (in the case of Switzerland, it is around 15 %, mainly food and energy). The calculation of core inflation is intended to show the long-term price trend, irrespective of short-term effects.
What prescriptions are used to fight inflation?
For central banks, it is important that inflation does not overshoot and that they counter it with the instruments at their disposal. In practice, interest rate hikes are the rule. The big challenge here is to find the right “dose” at the right time. This is because interest rate hikes have a dampening effect on economic growth, consumption falls and investments become more expensive.
What side effects may occur?
The current situation on the financial markets provides an example of the impact of rising interest rates in the wake of rising inflation figures. Central bank policy influences interest rates on the capital markets and investors adjust their expectations. Among other things, this leads to revaluations of stocks and bonds, i. e. price declines. Fighting inflation is like a balancing act.
The goal of reducing inflation is offset by weaker economic growth and higher interest costs for debtors.
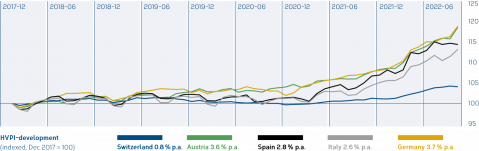
How has inflation developed over the medium term?
What principles should be followed in an inflationary environment?
The past has shown that there is no patent remedy for investors. The timing of a pickup in inflation is almost impossible to predict.
Inflation does not affect all asset classes equally. Studies show that so-called real assets (commodities, precious metals) can offer some protection. Liquidity and bonds are more affected, as inflation eats away the returns. In the case of equities, the great general uncertainty surrounding economic developments, falling margins and rising interest costs often have a negative impact.
Taking into account that inflation is difficult or impossible to forecast, a broadly diversified investment portfolio is recommended. A certain amount of liquidity ensures the ability to act and real assets can offer a certain protection against inflation in the long term.
LMM COMPASS
With our newsletter we provide information about the current situation on the financial markets, current investment topics and LMM.